Overview
The Integrated Biobank for Space Life Science (ibSLS) is a public open database jointly developed by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization (ToMMo), Tohoku University. It provides multi omics data, including transcriptome, metabolome, and phenotypes, derived from JAXA’s Mouse Habitat Unit (MHU) missions.
Biospecimens recovered from the MHU missions are also available upon request through JAXA Biospecimens Sharing Program. JAXA Tsukuba Space Center stores over 600 biospecimens remaining from spaceflight investigations since 2016. Biospecimens are available first to Japanese investigators, then to those in the USA under the Japan-US Open Platform Partnership Program (JP-US OP3).
Mission List
MHU-1
Mouse Epigenetics (PI: TAKAHASHI Satoru, University of Tsukuba)
Description
The MHU-1 mission is the first JAXA space mouse mission with artificial 1 g onboard environment to study various physiological changes that occur in adapting to microgravity. Two groups of six wild-type C57BL/6J male mice were launched to the International Space Station (ISS). One group was housed under microgravity (MG group, n = 6 mice) and the other group under artificial gravity of 1 g (AG) group (n = 6). The mice in the MG group were housed under microgravity for 35 days, while the mice in the AG group were housed under an artificial gravity of 1 g for 34.1 of those days. After the habitation on the ISS, the AG and MG mice were returned to Earth alive. The mice were then transported to a laboratory, and two days after their return (R+2) they were subjected to behavioral observations and tissue sampling for further analyses. Ground control (GC) mice were maintained in similar conditions as the flight mice (MG and AG mice) at the JAXA Tsukuba Space Center in Japan. Refer to the flagship paper[1] for further information.
Scheme
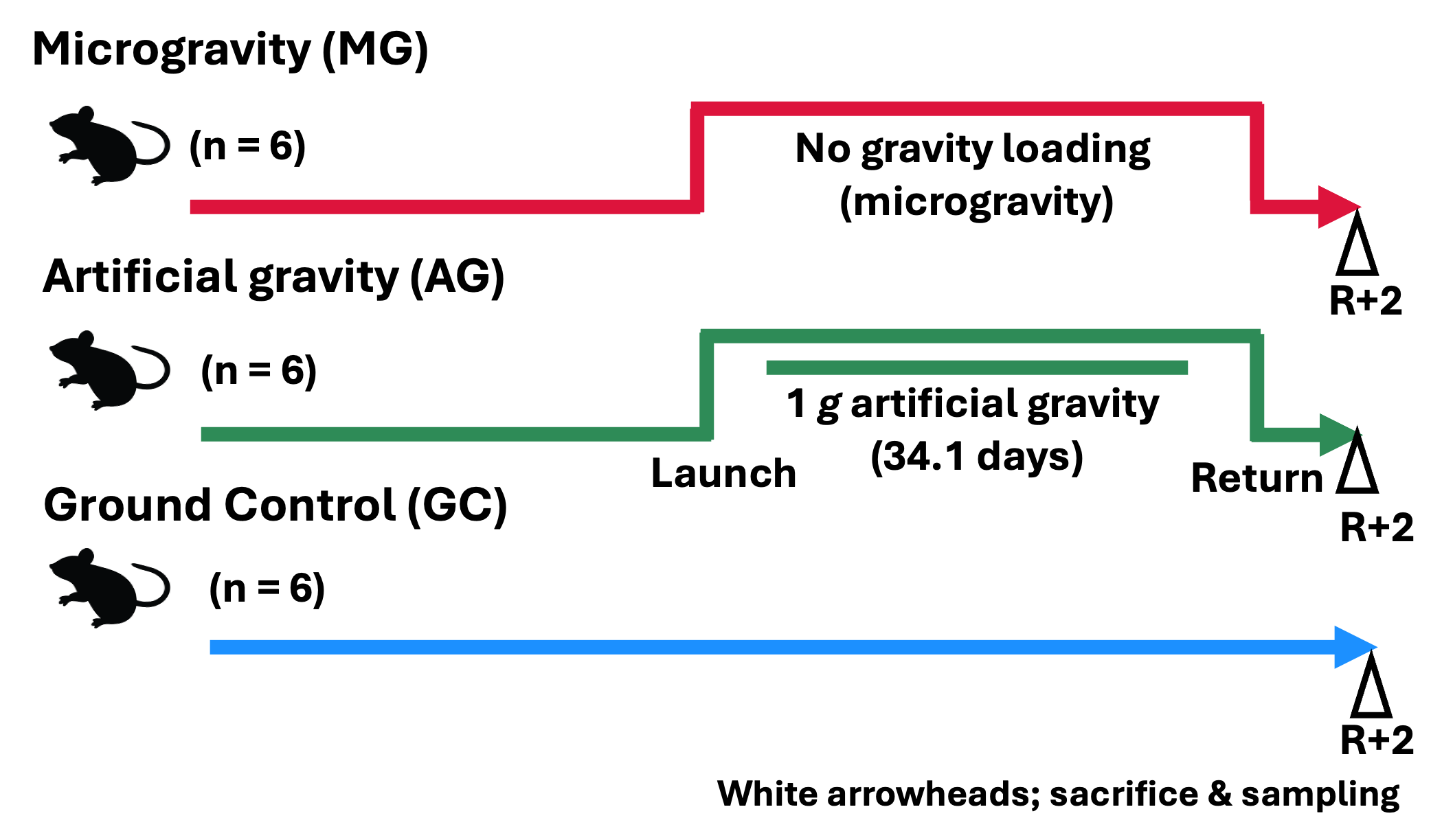
Flight Schedule
Vehicle Launch (GMT) Return (GMT) SpX-9 2016-07-18 2016-08-26 Animals
Species Strain Sex Mouse C57BL/6J Male Experimental Design
Group Status Gravity Age at launch Diet MG Flight Microgravity 8 weeks Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) AG Flight Artificial gravity (1 g) 8 weeks Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) GC Ground Control Normal gravity (1 g) 8 weeks Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) Tissue List
Tissue Sampling time point (days) Analysis Number of replicates Reference Lymph node R+2 RNA-Seq 3 2 Soleus muscles R+2 RNA-Seq 3 3, 6 Spine R+2 RNA-Seq 3 4 Spleen R+2 RNA-Seq 3 2 Thymus R+2 RNA-Seq 3 5 Samples available in Biospecimen sharing program link
Tissue Sampling time point Number of samples Treatment Storage Dorsal skin R+2 36 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Tail R+2 18 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Auricles R+2 18 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Experimental Procedure
Details of the sample preparation are provided in the paper.
RNA Sequencing
Tissue RNA extraction Library preparation Sequencing protocol Accession number Lymph node AGPC rRNA depletion 36bp, PE DRA008122 Soleus muscles AGPC rRNA depletion 36bp, PE DRA016428* Spine AGPC rRNA depletion 36bp, PE DRA013846 Spleen AGPC rRNA depletion 36bp, PE DRA008121 Thymus AGPC rRNA depletion 36bp, PE DRA008961 (*) The data were replaced from DRA010983 to DRA016428 in the 2025 update.
Acronyms
Category Acronyms General JAXA, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency; ISS, International Space Station; GMT, Greenwich Mean Time Group name GC, ground control; MG, microgravity; AG, artificial gravity Time point L, launch; R, return Procedure AGPC, acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction; PE, paired ended Reference
- Shiba D, Mizuno H, Yumoto A, Shimomura M, Kobayashi H, Morita H, Shimbo M, Hamada M, Kudo T, Shinohara M, Asahara H, Shirakawa M, Takahashi S. Development of new experimental platform 'MARS'-Multiple Artificial-gravity Research System-to elucidate the impacts of micro/partial gravity on mice.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 7;7(1):10837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10998-4.
- Horie K, Sasanuma H, Kudo T, Fujita SI, Miyauchi M, Miyao T, Seki T, Akiyama N, Takakura Y, Shimbo M, Jeon H, Shirakawa M, Shiba D, Yoshida N, Muratani M, Takahashi S, Akiyama T. Down-regulation of GATA1-dependent erythrocyte-related genes in the spleens of mice exposed to a space travel. Sci Rep. 2019 May 21;9(1):7654. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44067-9.
- Okada R, Fujita SI, Suzuki R, Hayashi T, Tsubouchi H, Kato C, Sadaki S, Kanai M, Fuseya S, Inoue Y, Jeon H, Hamada M, Kuno A, Ishii A, Tamaoka A, Tanihata J, Ito N, Shiba D, Shirakawa M, Muratani M, Kudo T, Takahashi S. Transcriptome analysis of gravitational effects on mouse skeletal muscles under microgravity and artificial 1 g onboard environment. Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 28;11(1):9168. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88392-4.
- Yoshikawa M, Ishikawa C, Li H, Kudo T, Shiba D, Shirakawa M, Muratani M, Takahashi S, Aizawa S, Shiga T. Comparing effects of microgravity and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the mouse ventral lumbar spinal cord. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jul;121:103745. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2022.103745. Epub 2022 Jun 2.
- Horie K, Kato T, Kudo T, Sasanuma H, Miyauchi M, Akiyama N, Miyao T, Seki T, Ishikawa T, Takakura Y, Shirakawa M, Shiba D, Hamada M, Jeon H, Yoshida N, Inoue JI, Muratani M, Takahashi S, Ohno H, Akiyama T. Impact of spaceflight on the murine thymus and mitigation by exposure to artificial gravity during spaceflight. Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27;9(1):19866. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56432-9.
- Okamura Y, Gochi K, Ishikawa T, Hayashi T, Fuseya S, Suzuki R, Kanai M, Inoue Y, Murakami Y, Sadaki S, Jeon H, Hayama M, Ishii H, Tsunakawa Y, Ochi H, Sato S, Hamada M, Abe C, Morita H, Okada R, Shiba D, Muratani M, Shinohara M, Akiyama T, Kudo T, Takahashi S. Impact of microgravity and lunar gravity on murine skeletal and immune systems during space travel. Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 20;14(1):28774. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79315-0.
- Shimomura M, Yumoto A, Ota-Murakami N, Kudo T, Shirakawa M, Takahashi S, Morita H, Shiba D. Study of mouse behavior in different gravity environments. Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 29;11(1):2665. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82013-w. Erratum in: Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 27;11(1):17563. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96312-9.
Unpublished Dataset
The unpublished data of MHU missions will be provided to academic and non-profit investigators upon request. The unpublished data list will be posted here with the data transfer agreement (DTA).
MHU-2
Multi-Omics (PI: OHNO Hiroshi, RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences)
Medical Proteomics (PI: HIRANO Hisashi, Yokohama City University)
Description
The MHU-2 mission is a JAXA's space mouse mission with two objectives: to understand how spaceflight affects the gut and immune system, including microflora and metabolites, and to determine whether the prebiotic fructooligosaccharide (FOS) improves gut and immune function during spaceflight. Two groups of six 9-week-old male mice were launched to the International Space Station. Each group was given a diet either with (FOS+) or without FOS (FOS-). One group was housed under microgravity (MG) and divided into two subgroups (n=3 MG_FOS- mice and n=3 MG_FOS+ mice). The other group of six mice was exposed to artificial 1 g (AG) and had two subgroups (n=3 AG_FOS- mice and n=AG_FOS+ mice). During habitation on the ISS, blood samples were collected by tail clipping at 17-18 days after launch (L+17/18). fecal pellets were also collected from all mice at each sampling time point. After habitation in the ISS, flight mice were returned to the Earth alive. Approximately two days after their return (R+2), the flight mice were subjected to behavioral observations and tissue sampling. Six ground control (GC) mice were divided into two groups (n=3 GC_FOS- mice and n=3 GC_FOS+ mice) and maintained in similar conditions as the flight mice at JAXA Tsukuba Space center in Japan. Fecal samples were collected at two sampling time points corresponding to L+17/18 and R+2. Refer to the flagship paper[1] for further information.
Scheme
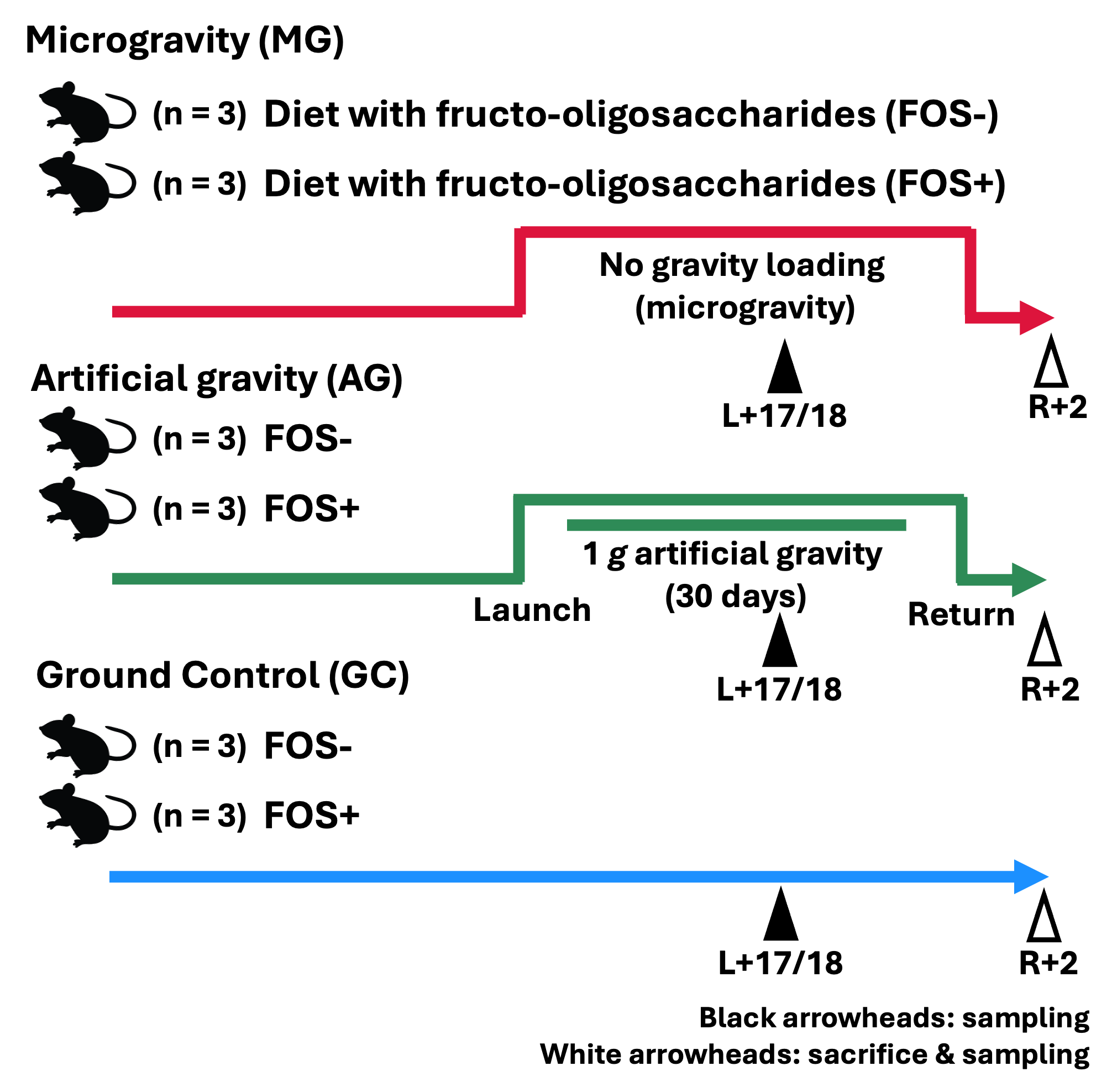
Flight Schedule
Vehicle Launch (GMT) Return (GMT) SpX-12 2017-08-13 2017-09-16 Animals
Species Strain Sex Mouse C57BL/6J Male Experimental Design
Group Status Gravity Age at launch Diet MG_FOS- Flight Microgravity 9 weeks AIN-93G10 without 5%FOS MG_FOS+ Flight Microgravity 9 weeks AIN-93G10 with 5%FOS AG_FOS- Flight Artificial gravity (1 g) 9 weeks AIN-93G10 without 5%FOS AG_FOS+ Flight Artificial gravity (1 g) 9 weeks AIN-93G10 with 5%FOS GC_FOS- Ground Control Earth gravity (1 g) 9 weeks AIN-93G10 without 5%FOS GC_FOS+ Ground Control Earth gravity (1 g) 9 weeks AIN-93G10 with 5%FOS Tissue List
Tissue Sampling time point Analysis Number of replicates Reference Liver R+2 RNA-Seq 3 3 Samples available in Biospecimen sharing program link
Tissue Sampling time point Number of samples Treatment Storage Femur skin R+2 17 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Auricles R+2 17 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Experimental Procedure
Details of the sample preparation are provided in the paper.
RNA Sequencing
Tissue RNA extraction Library preparation Sequencing protocol(**) Accession number Liver Spin column Poly(A) selection 150bp, PE GSE240751 Acronyms
Category Acronyms General JAXA, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency; ISS, International Space Station; GMT, Greenwich Mean Time Group name GC, ground control; MG, microgravity; FOS-, diet without fructo-oligosaccharide; FOS+, diet with fructo-oligosaccharide Time point L, launch; R, return Procedure PE, paired ended Sample share PFA, paraformaldehyde; MeOH, methanol Reference
- Matsuda C., Kato T., Inoue-Suzuki S., Kikuchi J., Ohta T., Kagawa M., Hattori M., Kobayashi H., Shiba D., Shirakawa M., Mizuno H., Furukawa S., Mukai C., Ohno H. Dietary intervention of mice using an improved Multiple Artificial-gravity Research System (MARS) under artificial 1 g. NPJ Microgravity. 2019 Jul 8:5:16. doi: 10.1038/s41526-019-0077-0. eCollection 2019.
- Horie K, Kato T, Kudo T, Sasanuma H, Miyauchi M, Akiyama N, Miyao T, Seki T, Ishikawa T, Takakura Y, Shirakawa M, Shiba D, Hamada M, Jeon H, Yoshida N, Inoue JI, Muratani M, Takahashi S, Ohno H, Akiyama T. Impact of spaceflight on the murine thymus and mitigation by exposure to artificial gravity during spaceflight. Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27;9(1):19866. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56432-9
- Kurosawa R, Sugimoto R, Imai H, Atsuji K, Yamada K, Kawano Y, Ohtsu I, Suzuki K. Impact of spaceflight and artificial gravity on sulfur metabolism in mouse liver: sulfur metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis. Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 8;11(1):21786. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01129-1.
- Kimura Y, Nakai Y, Ino Y, Akiyama T, Moriyama K, Aiba T, Ohira T, Egashira K, Yamamoto Y, Takeda Y, Inaba Y, Ryo A, Saito T, Kumagai K, Hirano H. Changes in the astronaut serum proteome during prolonged spaceflight. Proteomics. 2024 May;24(10):e2300328. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202300328.Epub 2024 Jan 7.
Unpublished Dataset
The unpublished data of MHU missions will be provided to academic and non-profit investigators upon request. The unpublished data list will be posted here with the data transfer agreement (DTA).
MHU-3
Mouse Stress Defense (PI: YAMAMOTO Masayuki, Tohoku University)
Description
The MHU-3 mission was designed to investigate the contribution of the transcription factor Nrf2 to the protection of mice against the stresses of spaceflight and to the maintenance of homeostasis during spaceflight. Six flight wild-type mice (n= 6 FL-WT mice) and six flight Nrf2 KO mice (n=6 FL-KO mice) on the C57BL/6J background were launched and stayed aboard the International Space Station (ISS) for 31 days. After habitation in the ISS, all mice were returned to the Earth alive and transported to a laboratory for analysis. Blood samples were taken from the tail vein at three timepoints, 17 days before launch (L-17), 18 days after launch (L+18) and 2 days after return (R+2). Blood samples from the inferior vena cava (IVC) and other tissue samples were collected on R+2. Blood sampling from one FL-WT mouse on L+18 was not conducted on the advice of the veterinarians due to a minor injury to the tail. Two groups of ground control (GC) mice were maintained in similar condition as the flight mice at the JAXA Tsukuba Space Center in Japan (n=6 GC-WT mice and n=6 GC-KO mice ). Refer to the flagship paper[1] for further information.
Scheme
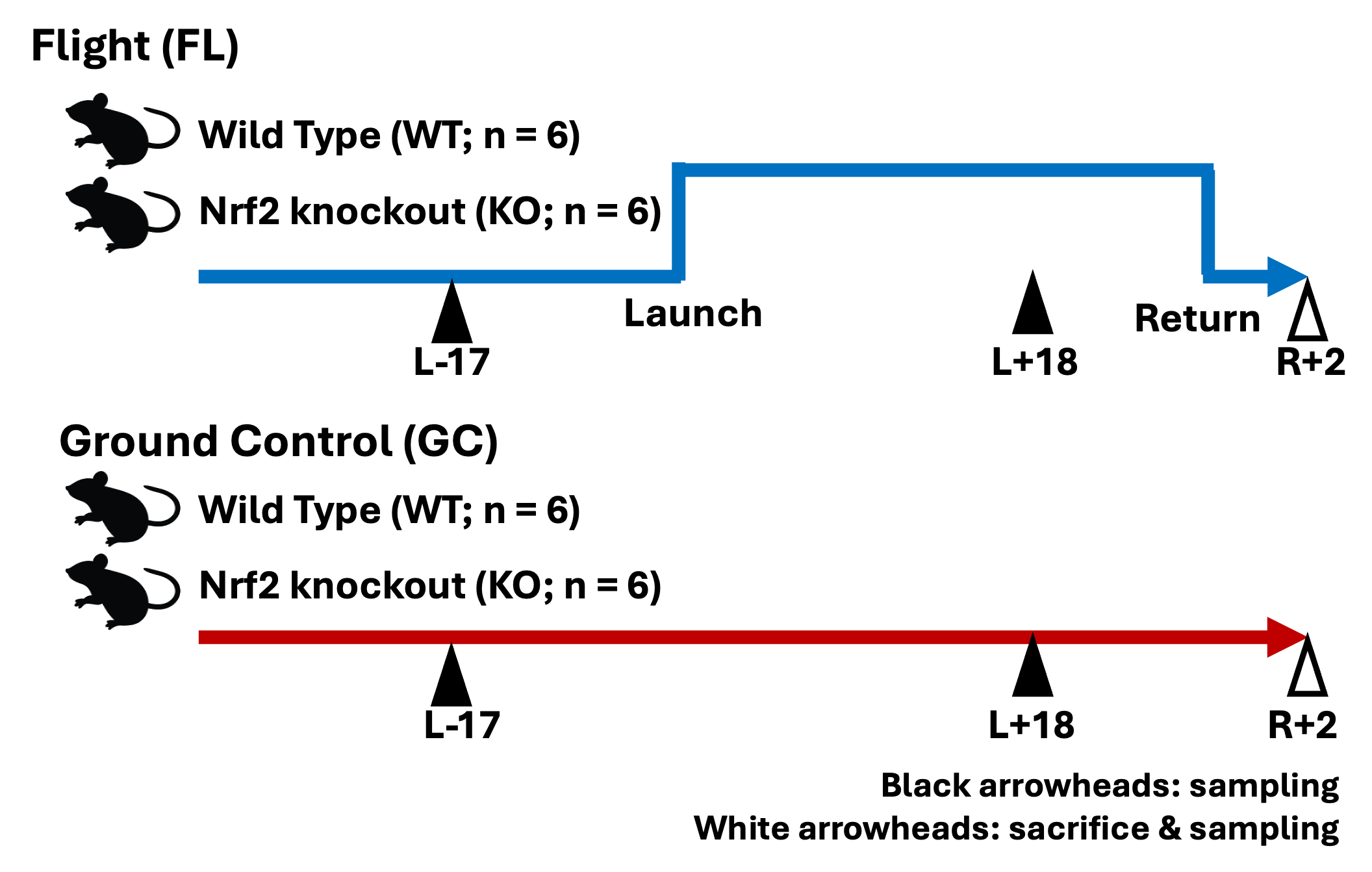
Flight Schedule
Vehicle Launch (GMT) Return (GMT) SpX-14 2018-04-02 2018-05-05 Animals
Species Strain Sex Mouse C57BL/6J Male Experimental Design
Group Genotype Status Gravity Age at launch Diet FL-WT Wild Type Flight Microgravity 8 weeks Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) GC-WT Wild Type Ground Control Normal gravity (1 g) 8 weeks Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) FL-KO Nrf2 Knockout Flight Microgravity 8 weeks Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) GC-KO Nrf2 Knockout Ground Control Normal gravity (1 g) 8 weeks Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) Tissue List
Tissue Sampling time point Analysis Number of replicates Reference Bone Marrow R+2 RNA-Seq 6 5 Brown adipose tissue R+2 RNA-Seq 6 1,2 Cerebrum R+2 RNA-Seq 6 1 Inguinal white adipose tissue R+2 RNA-Seq 6 1,2 Kidney R+2 RNA-Seq 3 1,4 Liver R+2 RNA-Seq 6 1 Mandibular Bone R+2 RNA-Seq 6 1 Plasma from Inferior vena cava R+2 Metabolome (NMR) 6 2 R+2 Metabolome (Mass spec) 6 Plasma from Tail vein L-17 Metabolome (Mass spec) 6 2 L+18 6 R+2 6 Soleus muscle R+2 RNA-Seq 3 3 Spleen R+2 RNA-Seq 6 1,5 Temporal Bone R+2 RNA-Seq 6 1 Thymus R+2 RNA-Seq 6 1 Samples available in Biospecimen sharing program link
Tissue Sampling time point Number of samples Treatment Storage Dorsal skin (left) R+2 24 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Dorsal skin (right) R+2 24 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Auricles (left) R+2 24 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Auricles (right) R+2 24 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Seminal gland (left) R+2 24 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Seminal gland (right) R+2 24 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Blood clot R+2 24 Fixed in 4% PFA and stored in MeOH -30℃ Experimental Procedure
Details of the sample preparation are provided in the paper.
RNA Sequencing
Tissue RNA extraction Library preparation Sequencing protocol Accession number Bone Marrow AGPC rRNA depletion 151bp, PE GSE240654 Brown adipose tissue AGPC Poly(A) selection 76bp, PE GSE152382 Cerebrum AGPC Poly(A) selection 76bp, PE GSE152382 Inguinal white adipose tissue AGPC Poly(A) selection 76bp, PE GSE152382 Kidney AGPC Poly(A) selection 76bp, PE GSE152382 Liver AGPC Poly(A) selection 76bp, PE GSE152382 Mandibular Bone AGPC Poly(A) selection 76bp, PE GSE152382 Soleus muscle AGPC rRNA depletion 36bp, PE DRA011091 Spleen AGPC Poly(A) selection 76bp, PE GSE152382 Temporal Bone AGPC Poly(A) selection 76bp, PE GSE152382 Thymus Spin column rRNA depletion 76bp, PE GSE152382 Metabolome (Mass spec)
Metabolome analyses of plasma samples from tail and IVC bloods were performed using the MxP Quant 500 Kit (Biocrates Life Sciences) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Tail plasma samples (5 µL) were used for the UHPLC-MS/MS analyses (Xevo TQ-S system, Waters).
Metabolome (NMR)
IVC plasma metabolites were extracted from 50 µL of plasma using a standard methanol extraction method. NMR experiments were performed at 298 K on a Bruker Avance 600-MHz spectrometer equipped with a CryoProbe and a SampleJet sample changer.
Acronyms
Category Acronyms General JAXA, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency; ISS, International Space Station; GMT, Greenwich Mean Time Group name GC, ground control; FL, flight; WT, wildtype; KO, Nrf2 knockout Time point L, launch; R, return Procedure AGPC, acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction; PE, paired ended; SE, single ended Sample share PFA, paraformaldehyde; MeOH, methanol Reference
- Suzuki T, Uruno A, Yumoto A, Taguchi K, Suzuki M, Harada N, Ryoke R, Naganuma E, Osanai N, Goto A, Suda H, Browne R, Otsuki A, Katsuoka F, Zorzi M, Yamazaki T, Saigusa D, Koshiba S, Nakamura T, Fukumoto S, Ikehata H, Nishikawa K, Suzuki N, Hirano I, Shimizu R, Oishi T, Motohashi H, Tsubouchi H, Okada R, Kudo T, Shimomura M, Kensler TW, Mizuno H, Shirakawa M, Takahashi S, Shiba D, Yamamoto M. Nrf2 contributes to the weight gain of mice during space travel. Commun Biol. 2020 Sep 8;3(1):496.doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01227-2.
- Uruno A, Saigusa D, Suzuki T, Yumoto A, Nakamura T, Matsukawa N, Yamazaki T, Saito R, Taguchi K, Suzuki M, Suzuki N, Otsuki A, Katsuoka F, Hishinuma E, Okada R, Koshiba S, Tomioka Y, Shimizu R, Shirakawa M, Kensler TW, Shiba D, Yamamoto M. Nrf2 plays a critical role in the metabolic response during and after spaceflight. Commun Biol. 2021 Dec 9;4(1):1381. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02904-6.
- Hayashi T, Kudo T, Fujita R, Fujita SI, Tsubouchi H, Fuseya S, Suzuki R, Hamada M, Okada R, Muratani M, Shiba D, Suzuki T, Warabi E, Yamamoto M, Takahashi S. Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (NRF2) deficiency accelerates fast fibre type transition in soleus muscle during space flight. Commun Biol. 2021 Jun 24;4(1):787. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02334-4.
- Suzuki N, Iwamura Y, Nakai T, Kato K, Otsuki A, Uruno A, Saigusa D, Taguchi K, Suzuki M, Shimizu R, Yumoto A, Okada R, Shirakawa M, Shiba D, Takahashi S, Suzuki T, Yamamoto M. Gene expression changes related to bone mineralization, blood pressure and lipid metabolism in mouse kidneys after space travel. Kidney Int. 2022 Jan;101(1):92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.09.031.
- Shimizu R, Hirano I, Hasegawa A, Suzuki M, Otsuki A, Taguchi K, Katsuoka F, Uruno A, Suzuki N, Yumoto A, Okada R, Shirakawa M, Shiba D, Takahashi S, Suzuki T, Yamamoto M. Nrf2 alleviates spaceflight-induced immunosuppression and thrombotic microangiopathy in mice. Commun Biol. 2023 Aug 25;6(1):875. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05251-w.
Unpublished Dataset
The unpublished data of MHU missions will be provided to academic and non-profit investigators upon request. The unpublished data list will be posted here with the data transfer agreement (DTA).
MHU-4
JAXA Moon-G mission 1 (PI: SHIBA Dai, JAXA)
Gravity Gateway Reflex (PI: MURAKAMI Masaaki, Hokkaido University)
Description
The MHU-4 mission is to evaluate the effect of artificial Lunar gravity (1/6 g) with a short radius centrifuge in the gene expression patterns in various organs and blood metabolites profiles during space flight. In 2019, six male mice of C57BL/6 were launched and maintained in the International Space Starion (ISS). During habitation in the ISS, the mice were loaded 1/6 g (0.167 g) of gravity (PG; partial gravity) for about 25 days. This condition mimics the gravity of the Moon as the most feasible future mission. The MHU-4 mission used the Multiple Gravity Research System with short radius (MARS-S), a device that generates artificial gravity with the same 15 cm radius as MHU-1 and 2. After habitation in the ISS, all mice were returned to the Earth alive and transported to a laboratory in the United States for analysis.
Blood samples were taken from the tail vein at two timepoints, 20 days after launch (L+20) and about 1 day after return (R+1). Blood samples from the inferior vena cava (IVC) and other tissues were collected on R+1. Tail blood samples as baseline for PG mice were obtained from six remaining mice at the time of launch (L+0). Ground control (GC) mice were maintained in similar conditions as the flight mice at the JAXA Tsukuba Space Center in Japan. Blood samples were collected at time points corresponding to L+0, L+20, and R+1. Refer to the flagship paper[1] for further information.Scheme
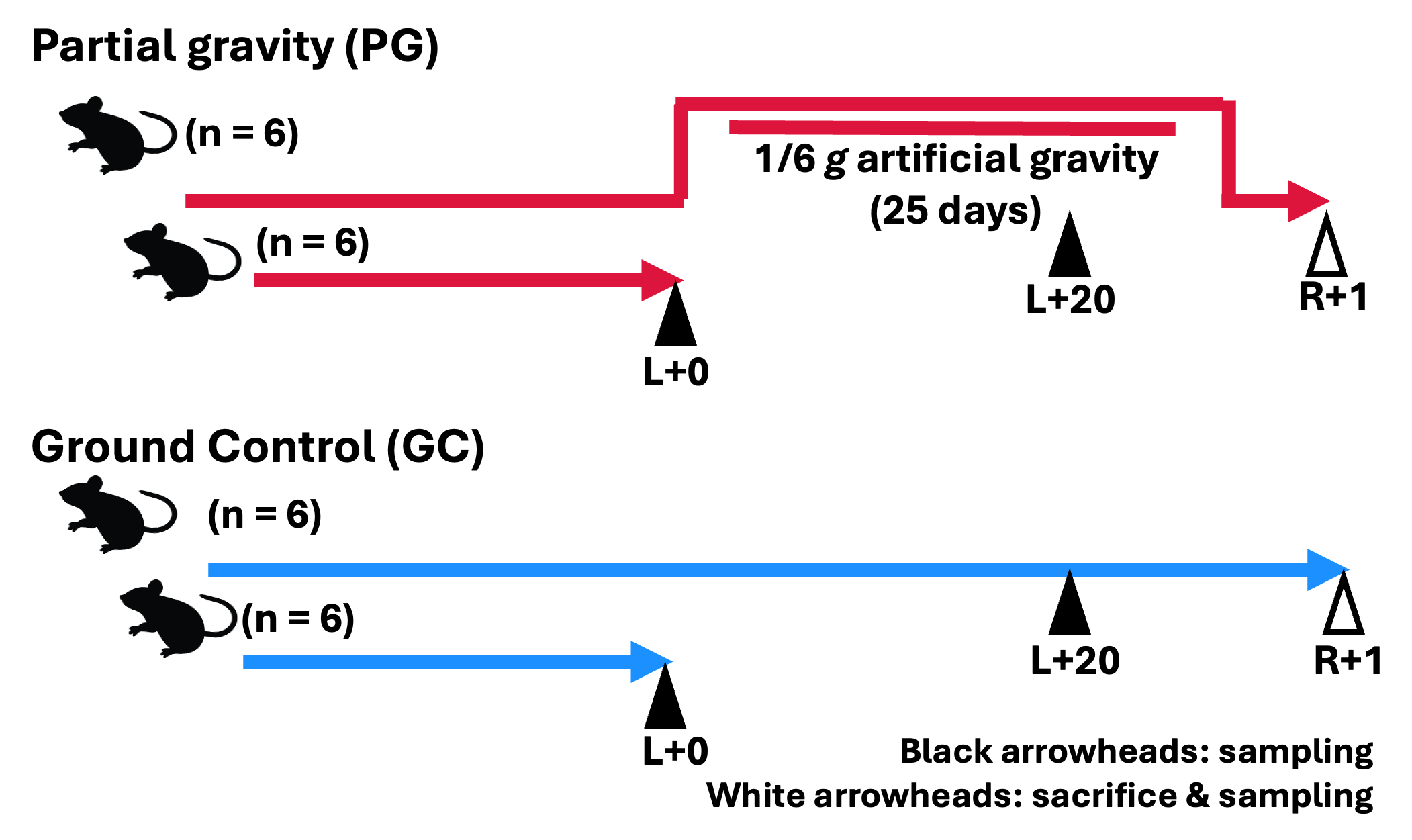
Flight Schedule
Vehicle Launch (GMT) Return (GMT) SpX-17 2019-05-04 2019-06-03 Animals
Species Strain Sex Age at launch Mouse C57BL/6J Male 9 weeks Experimental Design
Group Status Gravity Age at launch Diet PG Flight Artificial partial gravity (1/6 g) 9 weeks Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) GC Ground Control Normal gravity (1 g) 9 weeks Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) Tissue List
Tissue Sampling time point Analysis Number of replicates Reference Soleus muscle R+1 RNA-Seq 3 1,2 Plasma from Inferior vena cava R+1 Metabolome (Mass spec) 6 3 Metabolome (NMR) 6 3 Plasma from Tail vein L+0 Metabolome (Mass spec) 6 3 L+20 6 R+1 6 Samples available in Biospecimen sharing program link
In preparation.
Experimental Procedure
Details of the sample preparation are provided in the paper.
RNA Sequencing
Tissue RNA extraction Library preparation Sequencing protocol Accession number Soleus muscle AGPC rRNA depletion 36bp, PE DRA014378 Metabolome (Mass spec)
Metabolome analyses of plasma samples were performed using the MxP Quant 500 Kit (Biocrates Life Sciences) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Tail plasma samples (5 µL) were used for the UHPLC-MS/MS analyses (Xevo TQ-S system, Waters).
Metabolome (NMR)
IVC plasma metabolites were extracted from 50 µL of plasma using a standard methanol extraction method. NMR experiments were performed at 298 K on a Bruker Avance 600-MHz spectrometer equipped with a CryoProbe and a SampleJet sample changer.
Acronyms
Category Acronyms General JAXA, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency; ISS, International Space Station Group name GC, ground control; PG, partial gravity Time point L, launch; R, return Procedure AGPC, acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction; PE, paired ended; NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance Reference
- Hayashi T, Fujita R, Okada R, Hamada M, Suzuki R, Fuseya S, Leckey J, Kanai M, Inoue Y, Sadaki S, Nakamura A, Okamura Y, Abe C, Morita H, Aiba T, Senkoji T, Shimomura M, Okada M, Kamimura D, Yumoto A, Muratani M, Kudo T, Shiba D, Takahashi S. Lunar gravity prevents skeletal muscle atrophy but not myofiber type shift in mice. Commun Biol. 2023 Apr 21;6(1):424. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04769-3.
- Okamura Y, Gochi K, Ishikawa T, Hayashi T, Fuseya S, Suzuki R, Kanai M, Inoue Y, Murakami Y, Sadaki S, Jeon H, Hayama M, Ishii H, Tsunakawa Y, Ochi H, Sato S, Hamada M, Abe C, Morita H, Okada R, Shiba D, Muratani M, Shinohara M, Akiyama T, Kudo T, Takahashi S. Impact of microgravity and lunar gravity on murine skeletal and immune systems during space travel. Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 20;14(1):28774. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79315-0.
- Otsuki A, Aoki Y, Okada R, Kamimura D, Shiba D, Hishinuma E, Koshiba S, Katsuoka F, Kinoshita K, Suzuki T, Uruno A, Yamamoto M. ibSLS: A Biobank for Democratizing Access to Multi-Omics Data and Biospecimens from Spaceflight Research. bioRxiv 2025.09.08.675003. doi: 10.1101/2025.09.08.675003.
Unpublished Dataset
The unpublished data of MHU missions will be provided to academic and non-profit investigators upon request. The unpublished data list will be posted here with the data transfer agreement (DTA).
MHU-5
JAXA Moon-G mission 2 (PI: SHIBA Dai, JAXA)
Description
The MHU-5 mission is to evaluate the effect of artificial Lunar gravity (1/6 g) flight in the gene expression patterns in various organs and blood metabolites profiles during space flight. In 2020, the MHU-5 mission demonstrated the functionality of the Multiple Gravity Research System with long radius (MARS-L; 35 cm radius), an improved version of the artificial gravity generator, and is the counterpart to the MHU-4 mission. This device can generate centrifugal force by a longer radius than the MARS-S (15 cm radius) used in MHU-1, 2, and 4, and can equalize the gravity distribution in the cage. Using this set up, six male C57BL/6 mice were launched and maintained on the International Space Starion (ISS). During the habitation on ISS, the mice were loaded 1/6 g (0.167 g) of gravity (PG; partial gravity) for about 26 days. After the habitation, all mice were returned to the Earth alive and transported to a laboratory in the United States for analysis.
Blood samples from the inferior vena cava (IVC) and tail vein and other tissue samples were collected about 2 days after return (R+2). Tail blood samples as baseline for PG mice were obtained from six remaining mice at the time of launch (L+0). Ground control (GC) mice were maintained in similar conditions as the flight mice at the JAXA Tsukuba Space Center in Japan. Blood samples were collected at time point corresponding to L+0, and R+2. Refer to the flagship paper[1] for further information.Scheme
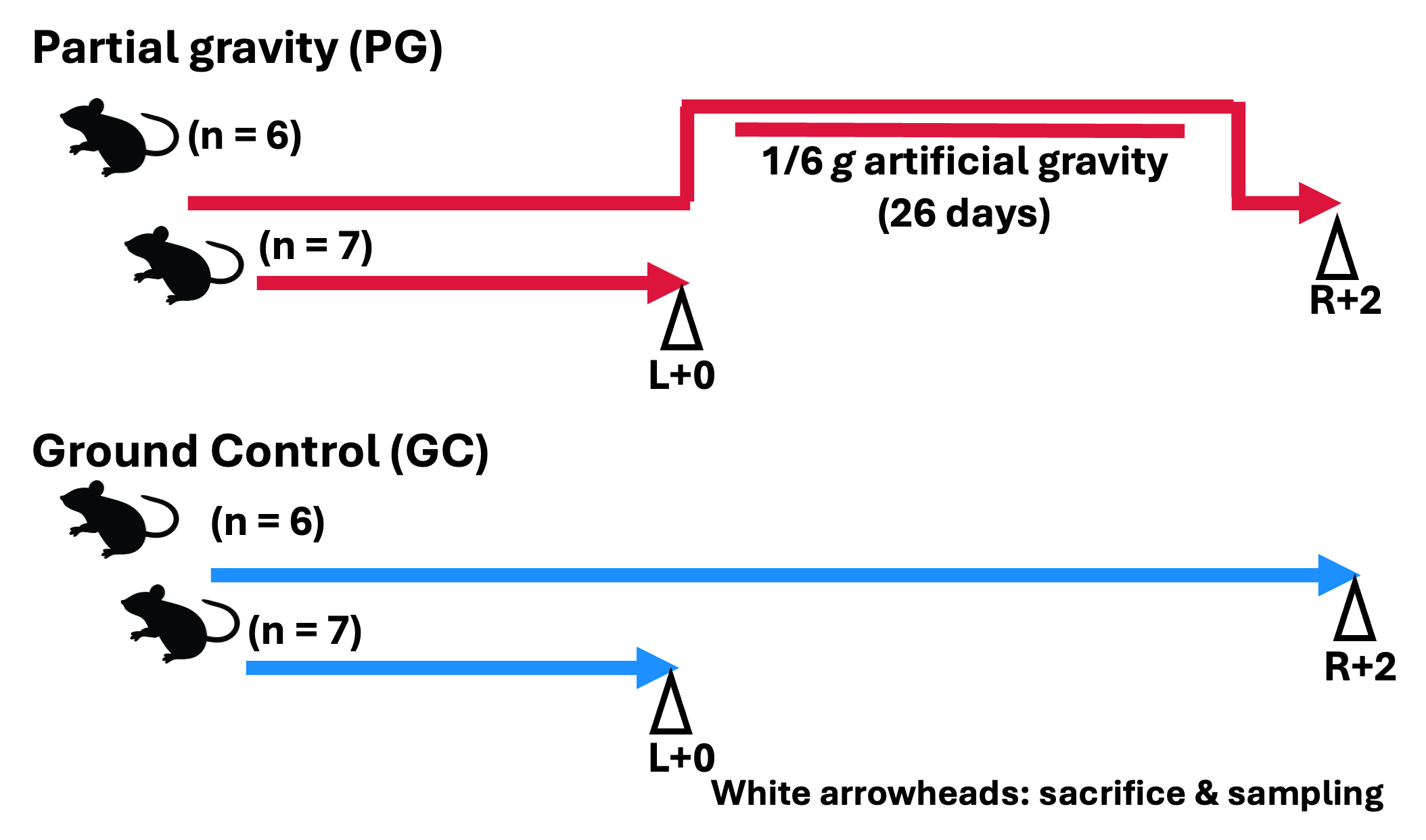
Flight Schedule
Vehicle Launch (GMT) Return (GMT) SpX-20 2020-03-06 2020-04-07 Animals
Species Strain Sex Age at launch Mouse C57BL/6J Male 9 weeks Experimental Design
Group Status Gravity Number Diet GC Ground Control Normal gravity (1 g) 13 Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) PG Flight Partial gravity (1/6 g) 13 Charles River Formula 1 (CRF-1) Tissue List
Tissue Sampling time point Analysis Number of replicates Reference Soleus muscle R+2 RNA-Seq 3 1,2 Plasma from Inferior vena cava R+2 Metabolome (Mass spec) 6 3 R+2 Metabolome (NMR) 6 3 Plasma from Tail vein L+0 Metabolome (Mass spec) 7 3 R+2 6 Samples available in Biospecimen sharing program link
In preparation.
Experimental Procedure
Details of the sample preparation are provided in the paper.
RNA Sequencing
Tissue RNA extraction Library preparation Sequencing protocol Accession number Soleus muscle AGPC rRNA depletion 36bp, PE DRA014378 Metabolome (Mass spec)
Metabolome analyses of plasma samples were performed using the MxP Quant 500 Kit (Biocrates Life Sciences) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Tail plasma samples (5 µL) were used for the UHPLC-MS/MS analyses (Xevo TQ-S system, Waters).
Metabolome (NMR)
IVC plasma metabolites were extracted from 50 µL of plasma using a standard methanol extraction method. NMR experiments were performed at 298 K on a Bruker Avance 600-MHz spectrometer equipped with a CryoProbe and a SampleJet sample changer.
Acronyms
Category Acronyms General JAXA, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency; ISS, International Space Station; GMT, Greenwich Mean Time Group name GC, ground control; PG, partial gravity Time point L, launch; R, return Procedure AGPC, acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction; PE, paired ended; NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance Reference
- Hayashi T, Fujita R, Okada R, Hamada M, Suzuki R, Fuseya S, Leckey J, Kanai M, Inoue Y, Sadaki S, Nakamura A, Okamura Y, Abe C, Morita H, Aiba T, Senkoji T, Shimomura M, Okada M, Kamimura D, Yumoto A, Muratani M, Kudo T, Shiba D, Takahashi S. Lunar gravity prevents skeletal muscle atrophy but not myofiber type shift in mice. Commun Biol. 2023 Apr 21;6(1):424. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04769-3.
- Okamura Y, Gochi K, Ishikawa T, Hayashi T, Fuseya S, Suzuki R, Kanai M, Inoue Y, Murakami Y, Sadaki S, Jeon H, Hayama M, Ishii H, Tsunakawa Y, Ochi H, Sato S, Hamada M, Abe C, Morita H, Okada R, Shiba D, Muratani M, Shinohara M, Akiyama T, Kudo T, Takahashi S. Impact of microgravity and lunar gravity on murine skeletal and immune systems during space travel. Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 20;14(1):28774. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79315-0.
- Otsuki A, Aoki Y, Okada R, Kamimura D, Shiba D, Hishinuma E, Koshiba S, Katsuoka F, Kinoshita K, Suzuki T, Uruno A, Yamamoto M. ibSLS: A Biobank for Democratizing Access to Multi-Omics Data and Biospecimens from Spaceflight Research. bioRxiv 2025.09.08.675003. doi: 10.1101/2025.09.08.675003.
Unpublished Dataset
The unpublished data of MHU missions will be provided to academic and non-profit investigators upon request. The unpublished data list will be posted here with the data transfer agreement (DTA).
Release History
2025-10-14ibSLS Version 4: Major Update. Transcriptome data from MHU-2, -4, and -5 missions, together with metabolome data from MHU-4 and -5 missions, were added. A new user interface, equipped with analysis tools, was implemented.2023-01-11ibSLS Version 3: Transcriptome data of MHU-1 mission2022-05-30ibSLS Version 2: Mouse plasma metabolome data of MHU-3 mission and linkage the mouse data with human cohort database jMorp2020-11-26ibSLS Version 1: Transcriptome data of MHU-3 mission2019-02-08JAXA and ToMMo signed a cooperation agreement to the realization of a healthy and long-lived society